![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Accessory Pigment |
An accessory pigment s a photosynthetic pigment that traps light energy and channels it to chlorophyll a, which initiates the reactions of photosynthesis. |
|
|
Colony |
~ A group of several individual organisms living together in close association. ~ Can exist separate |
|
|
Filament |
A slender threadlike object or fiber |
|
|
Alternation Of Generation |
~ Describes the life cycle of all algae and land plants ~ The life cycle alternated between diploid sporophtye generation and a haploid gametophyte generation |
|
|
Holdfast |
A branching body of an organism such as seaweed, which they use to attach to surfaces for support |
|
|
Sporophyte |
~ A spore producing generation of plant. ~ 2N |
|
|
Gametophyte |
~ A plant or phase of a plant's life cycle which bears gametes. ~ 1N |
|
|
Egg |
A structure which contains a fertilized zygote and nutrition for developing offspring. |
|
|
Sperm |
The male gamete which is involved in sexual reproduction which unites with the egg , resulting in a zygote. |
|
|
Thallus |
A structure in algae which makes up the main body of the algae. It lacks true roots, leaves and vascular tissue. |
|
|
Mitosis |
~ The process where a single cell divides resulting in generally two identical cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes and genetic content as that of the original cell. ~ Diploid (2n) |
|
|
Meiosis |
~ A form of cell division happening in sexually reproducing organisms, leading to the production of four haploid gametes ~ Haploid (n) |
|
|
Diploid |
~ 2N ~ Full, complete set of chromosomes |
|
|
Haploid |
~ N ~ Half set of chromosomes |
|
|
Mitosis Vs. Meiosis |
1. New cells are produced: Both 2. New cells have same number of chromosomes as parent: Mitosis 3. Parent is diploid: both 4. Daughter is haploid: meiosis 5. Occurs everywhere in the body: Mitosis 6. Produces sex cells or gametes: Meiosis 7. Chromosomes are copied before division: Both 8. Daughter all have same amount of chromosomes: Both 9. Daughters have more chromosomes than the parent: Niether 10. Is used in sexual reproduction: Meisois |
|
|
Characteristics Of Red Algae
|
Phylum: Rhodophtya |
|
|
Characteristics Of Green Algae
|
Phylum: Chlorophyta |
|
|
Characteristics of Brown Algae |
Phylum: Phaeophyta |
|
|
Chlamydomonas |
~ Grows in ponds, dilutes soil ~ Cup shaped chloroplast ~ 2 Flagella ~ Egg shaped ~ Unicellular |
|
|
Spirogyra |
~ Nicknamed "pond scum" ~ May use sexual or asexual reproduction ~ Conjugation ~ Macroscopic |
|
|
Protococcus |
~ Unicellular ~ Grows on tree trunks ~ Sex cells produced are identical looking (isogametes) |
|
|
Chlorella |
~ Unicellular ~ Food source for humans and orther living organisms |
|
|
Ulva |
~ Nicknamed "Sea lettuce" ~ Multicellular ~ (2 cells thick) ~ Isogamete (male + female sex cells look the same) ~ Zoospores ~ Alternation of generation as their lifecycle |
|
|
Volvox |
~ Connects between individuals allowing for communication ~ A few cells are specialized for reproduction |
|
|
Reproduction In Spirogyra |
~ Asexual Reprodution: by fragmentation or crosswise fission ~ Sexual reproduction where neighboring cell's filaments touch which produces swellings and the ends dissolve to produce an opening which is called the conjugation tube. The cytoplasm of one cell goes through this tube and unites with that of the other cell, forming a zygote and a thick wall forms around the zygote. When conditions are favorable, the zygote will undergo meisosis and will produce 4 hapolid spore, 3 of which will die, and the remaining will grow into a new filament |
|
|
Life Cycle Of Ulva |
~ Ulva is a common floating or attached, shallow water, marin, tropical or temperate, green alage known as "sea lettuce". Adult thalli leaves are only 2 cells thick, thus making the thalli transparent. ~ Ulva exhibits isomorphic alternation of generations which means the gametophyte and sporophyte generations look the same. |
|
|
Life Cycle Of Ulva (Diagram) |
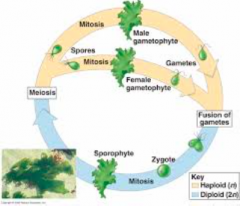
|
|
|
Chlamydomonas |
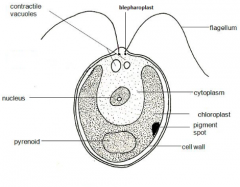
|
|
|
Spirogyra |

|
|
|
Protococcus |

|
|
|
Chlorella |

|
|
|
Ulva |

|
|
|
Volvox |
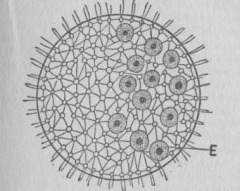
|
|
|
Reproduction in Spirogyra |

|
|
|
Ancestral Green Algae Vs. Modern Plants |
1. Have cell walls made of cellulose: Both 2. Live mostly in aquatic environments: Green Algae 3. Has alternation of generations in its life cycle: Both 4. Develop a cell plate during cell division: Both 5. Stores food as starch: Both 6. Have photosynthetic pigments contained in chloroplasts: Both
|
|
|
Life Cycle Of Moss |
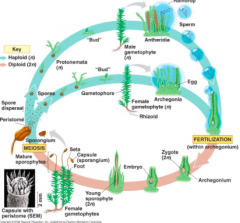
|
|
|
Vascular Tissue "Conducting Tissue" |
~ Contains Xylem, Phloem ~ Allows plants to live in a land environment however there are problems which plants need to overcome: 1. Transport & Body Support - Use vascular tissue to transport - Have rigid cells walls that provide support to the plant 2. Water Loss & Gas Exchange - Most plants have a waxy cuticle on the leaves and stems which prevent water loss and may also prevent the exchange of gas. To compensate for this plants have pores which allow for gas exchange 3. Nutrients and Reproduction - In sexual reproduction and sperm transfer, the sperm are transferred through air currents and insects and the gametes developed an outer layer of protective cells to prevent them from drying out - To absorb nutrients, plants have developed roots |
|
|
Xylem |
Conducts water + nutrients upward from the roots |
|
|
Phloem |
Conducts the products of photosynthesis (sugars) downward from the leaves |
|
|
Leaf Of A True Plant |

~ The stomata allows for gas exchange, CO2 moves into the leave and O2 moves out. Water is also lost through the stomata. ~ Stomata closed during the day to avoid excess water loss and open at night for gas exchange |
|
|
Photosynthesis Reaction |
CO2 (gas) + H20 + Sunlight ---> C6H12O6 + O2 (gas) |
|
|
Life Cycle Of A Fern |
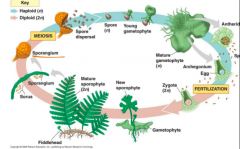
|
|
|
Antheridium |
Is a haploid structure containing male gametes |
|
|
Archegonium |
Is a haploid structure of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the female gamete |
|
|
Sporangium |
Spore case, within which asexual spores are produced. |
|
|
Spores |
A dormant, reproductive cell formed by certain organisms. It is thick-walled and highly resistant to survive under unfavorable conditions so that when conditions revert to being suitable it gives rise to a new individual. |
|
|
Fiddlehead |
The young, curled, edible frond of certain ferns. |
|
|
Zygote |
A cell in diploid state following fertilization |
|
|
Rhizome |
A horizontal underground stem |
|
|
Rhizoid |
Rhizoid is non-cellular thread like extension of some plants and they have been evolved during evolution of plants to land habitat for absorption and conservation of water. |
|
|
Sorus (sing.) or Sori (plural) |
~ Found on the underside of the frond ~ They produce the sporangium
|
|
|
Where In the Fern Does Meiosis Occur? |
~ Meiosis occurs in the sporangium and results in the spores |
|
|
Fertilization |
A process in sexual reproduction that involves the union of male (sperm) and female (ovum) gametes (each with a single, haploid set of chromosomes) to produce a diploid zygote. |
|
|
Comparison Between Moss and Fern |
Moss: Dominant Generation: Gametophyte Nutrition Dependance: Sporophyte depends on gametophyte Vascular Tissue? No Ferns: Dominant Generation: Sporophyte Nutrition Dependance: Young sporophyte depends on the gametophyte until it can photosynthesis on it's own Vascular Tissue? Yes |
|
|
Frond |
The leave of a fern |
|
|
Bryophyte |
Bryophytes are most commonly mosses, they are restricted to mostly moist environments. Considered non-vascular, due to a lack of vascular tissue. |
|
|
Tracheophyte |
A vascular plant contains the conducting systems which consist of xylem for conveyance of water and phloem for conveyance of food such as sugar. |
|
|
Ecological Roles Of Mosses |
~ Create organic matter and maker local habitats more suitable for seed bearing plants ~ Water retention ~ Land stabilitization ~ Shelter and humidity for a diverse group of invertebrates ~ Integrated part of the food web |
|
|
Economical Roles Of Mosses |
~ Florist Trade ~ Sphagaum Moss is a key ingredient in peat moss - Peat mosses accumulate in deposits that may be several hundred meters thick - Used as fuel, as a soil addative and in the production of whiskey ~ In world war II, sphagnum moss was used as first-aid dressings on soldier's wounds |
|
|
Ecological and Economical Roles Of Ferns |
Ecological: ~ Holds and forms the soil ~ Prevents soil erosion Economical: ~ Food (fiddleheads) ~ Azolla (mosquito fern) is used as biological fertilizer for rice paddies in Southwest Asia. It is able to fix nitrogen in the air to be used by other plants ~ Landscaping, horiculture and the florist industry ~ useful in removing heavy metals like arsenic from the soil ~ Decomposed ferns are a component of coal formation |
|
|
Animalike Protsist |
~ Members of phylum ciliophora, such as paramecium, are known as ciliates. Almost all ciliates use cilia for movement ~ Members of phylum Zoomastigina are known as flagellates because they use flagella for movement ~Members of the phylum Sporozoa, such as plasmodium, reproduce by means of spores. They are nonmotile and parastic ~ The phylum Sarcodina includes amebas and foraminifers. They use pseudopods for feeding and movement. |

