![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Normal size of trachea ? |
Not more than 2.5 cm or less than the adjacent vertebral body |
|
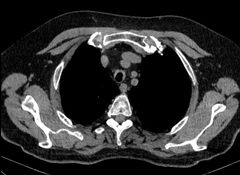
Finding Diagnosis |
Long segment anterior and lateral tracheal wall thickening with sparing of the posterior tracheal wall. Relapsing polychondritis |
|
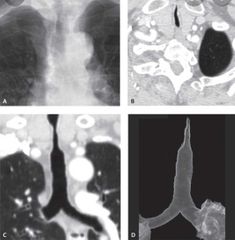
Finding Diagnosis |
Focal Narrowing of the trachea Subglottic post intubation stenosis |
|
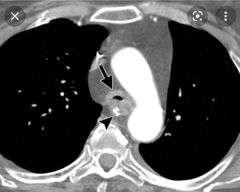
Finding Diagnosis |
Circumferential wall thickening of the trachea with calcification ( usually no calcification) Wegner granulomatosis |
|
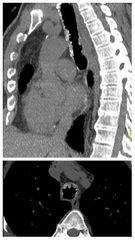
Finding Diagnosis |
Diffuse nodular calcifications in the tracheal antero-lateral walls. There is no relevant tracheal stenosis. The appearances are much more irregular than that seen with normal cartilage calcification. Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica ( TBO) |
|
|
Two condition spares the posterior tracheal ring? |
Relapsing polychondritis Tracheobronchopathic osteochondroplastica ( TBO) |
|
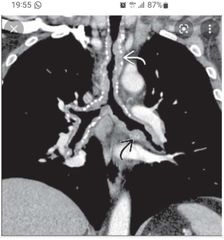
Finding Diagnosis |
Irregular wall thickening with calcifications |
|
|
Age of onset of TBO? |
Older than 50 years |
|
|
When I say saber sheath trachea you say? |
COPD |
|
|
Subtypes of tracheobronchial Carcinoid? 3 |
Typical Carcinoid Atypical Carcinoid Small cell and large cell tracheobronchial Carcinoid |
|
|
Differences BTW Typical Carcinoid Atypical Carcinoid Small and large cell Carcinoid In terms of: location Grade of tumor Age of onset Size |
Typical ( at bifurcation, low grade, 50s , < 3 cm.) Atypical ( peripheral distal to segmental bronchus, intermediate grade, 60s, > 3cm) associated with smoking Small cell and large cell ( not in the airway) Malignant ( high grade) Small ~3.5 cm, peripheral Large > 4 cm, central mediastinal involving hilum |
|
|
Bronchial Carcinoid vs GI Carcinoid in metastasis to the eye? |
Bronchial mets to the uveal tract ( inside orbit) GI Carcinoid mets to the extraocular muscles ( outside orbit) |
|
|
Clinical presentation of endobronchial Carcinoid? 2 |
Obstruction symptoms Hemoptysis ( highly vascular) |
|
|
Nuclear radiotracer for Carcinoid? |
Ocetreo PET is cold |
|
|
How common endobronchial Carcinoid cause Carcinoid syndrome? And if it does which valves are affected vs GI Carcinoid? |
Rarely Bronchial Carcinoid ( mitral and aortic) GI Carcinoid ( tricuspid and pulmonary) |
|
|
Most common malignancy of trachea? Second most common? |
Squamous cell carcinoma ( smoking ) Adenoid cystic carcinoma ( not associated with smoking) |
|
|
Bronchial Adenoid cystic carcinoma Location ? Appearance? |
Main or lobar bronchus Upper trachea posterolateral Variable appearance Nodule, thickening or mass |
|
|
Most common benign airway tumor? Causes if single or multiple? |
Squamous cell papilloma Single smoking Multiple HPV |
|
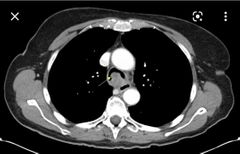
Likely diagnosis |
Adenoid cystic carcinoma |
|
|
Pathophysiology of cystic fibrosis ? |
Damaged sodium potassium pump ( thick secretions no clearance recurrent pneumonia) |
|
|
Features of cystic fibrosis? 4 |
Upper lobe predominance Cylindrical then varicoid bronchiectasis Finger in gloves appearance when plugged by mucus Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
|
|
Pathophysiology of primary ciliary dyskinesia? |
Cilia not working No clearing of secretions Recurrent infections Kids chronic sinusitis Boys sperms can't swim Girls ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
Radiological features of primary ciliary dyskinesia? |
Lower lobe bronchiectasis Chronic sinusitis 50% Kartagner syndrome |
|
|
What is Williams Campbell syndrome ? |
Cystic bronchiectasis due to cartilage deficiency |
|
|
Syndrome causes tracheobronchomegaly? > 3 cm |
Mounier- kuhn syndrome |
|
|
Ddx of small airway disease ? 5 |
RB ILD ( smokers) Infectious Bronchiolitis Subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis Constrictive Bronchiolitis Follicular Bronchiolitis |
|
|
Classic appearance of small airway disease ? |
Areas of air trapping ( mosaic attenuation) |
|
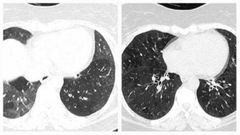
Findings Diagnosis |
There is widespread mosaic attenuation in both lungs, well demonstrated as areas of air trapping on the expiratory images, associated with cylindrical bronchiolectasis in the posterior segments of the left lower lobe. These features favour small airway disease. |
|
|
Risk factors for developing follicular Bronchiolitis? Appearance of follicular Bronchiolitis? |
Sjogren syndrome Rheumatoid arthritis Centrilobular ground glass nodules like hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
|
|
Risk factors of developing constrictive Bronchiolitis? 5 Appearance ? |
Viral illness Transplant patients Drug reaction Inhalation injury DIPNECH ( diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia) Swyer-James hyperlucent lung |
|
|
Aspiration pneumonia in Supine Upright position ? |
Supine ( posterior segments of the upper lobes, superior segment of lower lobes ) Upright ( basal segments of lower lobes) |
|
|
Complications of aspiration pneumonia? 2 |
Empyema and bronchopleural fistula |
|
|
What you call it when aspiration of gastric acid ? |
Mandelson's syndrome ( airspace opacity if massive looks like pulmonary edema) |
|
|
Aspiration of water or neutralised gastric contents Radiology appearance? |
Fleeting opacity ( will resolve in few hours) |

