![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
DRAW THE COAG CASCADE
|
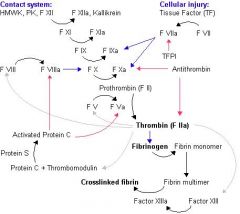
-
|
|
|
|
Name 4 major events in hemostasis
|
1.) Vascular constriction
2.) Platelet plug formation 3.) Fibrin formation 4.) Fibrinolysis |
|
|
|
Etiology of acute coagulopathy in trauma
|
activation of protein C and fibrinolysis
|
|
|
|
Where is thromboxane (TXA2) from?
|
Platelets
|
|
|
|
Where is prostacyclin from?
|
Endothelium
|
|
|
|
What is the action of PGI2
|
decreases platelet aggregation and promotes vasodilation
|
|
|
|
Name 3 actions of TXA2
|
1.) increases platelet aggregation and promotes vasoconstriction
2.) triggers Ca release in plts to expose GpIIb/IIIa receptor --> plt-plt binding 3.) Activates PIP system to further increase calcium |
|
|
|
Name 2 potent vasoconstrictors
|
endothelin
serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) |
|
|
|
How do endothelial cells prevent clotting?
|
Interfere with platelet recruitment by inactivating ADP
|
|
|
|
Action of heparin sulfate
|
catalyzes inhibition of thrombin by antithrombin
|
|
|
|
Action of thrombomodulin
|
down-modulates coagulation process through activation of protein C
|
|
|
|
Percentage of circulating platelets that may be sequestered in spleen
|
30%
|
|
|
|
Average life span of platelets
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
|
Describe primary hemostasis
|
intimal injury exposes subendothelial collage which platelets adhere to via vWF
|
reversible
|
|
|
Action of vWF
|
binds to GPI/IX/V on platelet membrane
|
|
|
|
Name 2 principal mediators in platelet aggregation
|
ADP and serotonin
|
|
|
|
2 ways that platelets contribute to hemostasis
|
Forming hemostatic plug and contributing to thrombin formation
|
|
|
|
Which receptor allows platelet-collagen binding?
|
GpIb receptor
|
|
|
|
What is TXA2 derived from?
|
Arachidonic acid (from plts) -> prostaglandin G2 --> PGH2 --> TXA2
|
|
|
|
Action of ASA
|
Irreversibly inhibit platelet COX
|
|
|
|
Action of NSAIDs
|
Reversibly blocks platelet COX
|
|
|
|
Describe second wave of platelet aggregation
|
Release reaction of ADP, calcium, serotonin, TXA2, alpha-granule proteins
|
|
|
|
What is a required cofactor in the second wave of platelet aggregation?
|
Fibrinogen which acts as a bridge for GPIIb/IIIa receptor (plts form a plug that is no longer reversible)
|
|
|
|
Site of secretion and action of thrombospondin
|
alpha granules and stabilizes fibrinogen binding to activated platelets
|
|
|
|
Action of platelet factor 4
|
potent heparin antagonist
|
|
|
|
4 Inhibitors of second wave of platelet aggregation
|
ASA, NSAIDS, cAMP, NO
|
|
|
|
Result of release reaction
|
Alterations in phospholipids of platelet membrane that allow calcium and clotting factors to bind to platelet surface (aka platelet factor 3)
|
|
|
|
Define prothrombin complex
|
X, V, Ca, Platelet factor 3, and prothrombin which forms on platelets
|
|
|
|
Action of prothrombin complex
|
Catalyzes formation of thrombin
|
|
|
|
Convergence point of intrinsic and extrinsic pathways
|
Factor X
|
|
|
|
What inhibits Factor X
|
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor
|
|
|
|
What is the key to coagulation?
|
Thrombin!
1.) Converts fibrinogen to fibrin and FSP 2.) Activates factors V and VIII 3.) Activates platelets |
|
|
|
What helps crosslink fibrin?
|
XIII
|
|
|
|
Describe intrinsic pathway
|
exposed collagen + prekallikrein + HMW kininogen + factor XII --> activates XI --> activates IX + VIII --> activate X + V --> convert prothrombin (factor II) to thrombin
|
|
|
|
Extrinsic pathway
|
Tissue factors from injured cells + factor VII --> activate X + V --> convert prothrombin to thrombin
|
|
|
|
Which factor has the shortest half life
|
Factor VII
|
|
|
|
Which factors are labile without any activity in blood but retained in FFP?
|
V and VIII
|
|
|
|
Vitamin K dependent factors
|
II, VII, IX, X, proteins C & S
|
|
|
|
How long does Vit K take to work?
|
6 hours
|
|
|
|
How long does FFP take to work and how long does it last for?
|
Immediate; 6 hours
|
|
|
|
Half life of RBCs
|
120 days
|
|
|
|
Half life of PMNs
|
1-2 days
|
|
|
|
Key to anticoagulation
|
AT III
|
|
|
|
Actions of AT III
|
Inhibits thrombin
Inhibitors factors IX, X, XI Bound by heparin |
|
|
|
Actions of protein C
|
Degrades factors V and VIII and fibrinogen
|
|
|
|
Action of protein S
|
Protein C cofactor
|
|
|
|
Fibrinolysis involves?
|
Tissue plasminogen activator, plasmin, Alpha-2 antiplasmin
|
|
|
|
Where is tissue plasminogen activator released?
|
endothelium
|
|
|
|
Action of plasmin
|
Degrades Factors V, VIII, fibrinogen, fibrin --> lose platelet plug
|
|
|
|
Natural inhibitor of plasmin
|
Alpha-2 antiplasmin (released from endothelium)
|
|
|
|
What blood product contains the highest concentration of vWF VIII?
|
Cryoprecipitate
|
|
|
|
What does FFP comprise of?
|
high levels of all factors, protein C & S, AT-III
|
|
|
|
Action of ddAVP & conjugated estrogens
|
Cause release of VIII and vWF from endothelium
|
|

