![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Type I DM effect on fetus.
|
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (probably long-standing DMI with retinal or renal complications)
10% of DM in pregnancy |
|
|
Screening Test for GDM
When is it performed? Cutoffs? |
Performed at 24-28 weeks
50g glucose orally when fasting, and measure glucose at 1 hour If >130, do GTT (must then have 2 values above reference range!) If >195, GTT = POSITIVE |
|
|
Risk factors for diabetic embryopathy.
HbA1C cutoffs. Prevention? |
Poor control with hypergly
10 year hx of DM Diabetic vascular dz HbA1C<8.5%: rate of defects = 3.4% HbA1C>8.5%, rate of defects = 22.4% Prevention must occur early on, not at 24 weeks, relevant to known diabetics! |
|
|
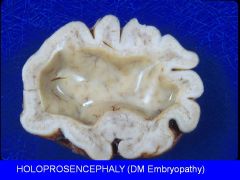
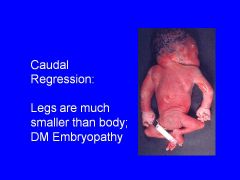
Signs of diabetic embryopathy.
|
Caudal regression
NT defects Holoprosencephaly CV anomalies |
|
|
Diabetic fetopathy vs embryopathy (general: occurrence)
|
Diabetic fetopathy can occur with either preexisting or gestational diabetes
Diabetic embryopathy occurs almost exclusively with preexisting diabetes |
|
|
Fetal response to hyperglycemia.
|
Inc'd fetal insulin-->growth stimulus (confined to fetal/neonatal period)
Results in fetal macrosomia |
|
|
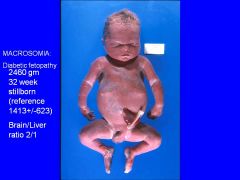
Define fetal macrosomia.
Include brain/liver ration. |
Weight >4000g (at birth)
*exceeds 90th percentile Accompanied by visceromegaly, but brain spared Placenta is also large Brain/liver ratio: 2/1 (normally 3/1) |
|
|
Effect of diabetes on CV system.
|
Hypertrophic CM involving BOTH ventricles
May show asymmetrical septal hypertrophy Resolves if infant survives |
|
|
How does diabetes cause fetal hypoxia?
|
Maternal causes: vasculopathy, ketoacidosis (alters HbO2 dissociation curve)
Dec'd uteroplacental blood flow due to hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, or pre-eclampsia Fetal Causes: hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, ketonemia |
|
|
What is Erb's palsy?
|
Shoulder dystocia due to macrosomia and subsequent brachial plexus injury.
|
|
|
Glucose cutoffs for postnatal hypoglycemia.
|
Glucose values:
Low birth weight <20 Full sized: <30 in first 48 hours; then <40-50 |
|
|
Effects of DM on fetal pancreas.
Electrolyte effects? |
enlarged islets (hypertrophy)
pleomorphism hyperchromatism of BETA-CELL nuclei EOSINOPHILS in and around islets HYPOCALCEMIA FOR SOME REASON |
|
|
Effect of DM on lung development.
|
Delayed lung development and delayed surfactant production-->RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|
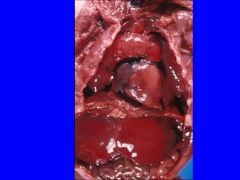
Placenta in DM; this is large, weighing 1015 g. Mean placental weight is 432g at 37 weeks.
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

