![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteoarthritis is typified by
|
erosion and inflammation of hyaline (articular) cartilage usually of the weight bearing joints
|
|
|
Cartilage and bone are both
|
specialized connective tissues
|
|
|
Cartilage has an extracellular matrix (ECM) designed to
|
resist mechanical stress
|
|
|
Most long bones are formed in the embryo as
|
cartilage
|
|
|
Bone replaces cartilage in long bones via
|
endochondral ossification
|
|
|
intramembranous ossification
|
type of bone formation where most flat bones of the body are formed from membranous sheaths
|
|
|
-Cartilage is an avascular tissue consisting of
-Cells receive nourishment via |
-chondrocytes & extracellular matrix (ECM)
-diffusion of nutrients from surrounding blood vessels, through the matrix |
|
|
Collagen is solid yet pliable due to
|
high glycosaminoglycan (GAG) to type II collagen ratio in ECM
|
|
|
3 types of cartilage
|
Hyaline
Elastic Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage appears
|
glassy and bluish when alive
|
|
|
What is the is the most abundant cartilage type?
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Location of hyaline cartilage in body
|
-Articular ends
-Respiratory tract (trachea, maintains opening) -Ventral ends of ribs -Temporary skeleton for endochondral bone development of long bones |
|
|
Which type of cartilage has a perichondrium?
|
-hyaline, *except at articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
-elastic |
|
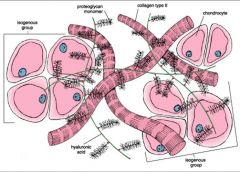
ECM in hyaline cartilage:
-predominant fibril component -others |
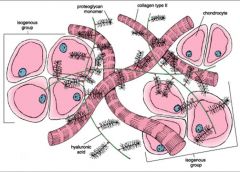
-type II collagen
-GAGs, and multiadhesive glycoproteins -Proteoglycans (aggrecan molecules): Chondroitin sulfate & keratin sulfate chains (each GAGs) attach to a core protein, which then attach via linker proteins to hyaluronine to make up aggrecan (a proteoglycan) |
|
|
Matrix is highly hydrated
-Much of this water is tightly bound to ___ and imparts ___ -Some of the water is bound loosely allowing |
-aggrecan-hyaluronan aggregates; resilience
-diffusion and transfer of metabolites through the ECM |
|
|
cells of hyaline cartilage that produce matrix material that surrounds them
|
isogenous groups
|
|
|
60-80% of the weight of hyaline cartilage is water – mostly bound to the ___ aggregates
|
hyaluronate proteoglycan
|
|
|
Matrix of hyaline cartilage is acidophilic or basophilic? Why?
|
-basophilic
-sulfated proteoglycans |
|
|
Matrices surrounding chondrocytes of isogenous groups
-Capsular or pericapsular matrix -Territorial matrix -Interteritorial matrix |
-area with strongest basophilia; immediately surrounding the chondrocytes
-is more removed from chondrocytes and stains less intensely compared to the capsular matrix, surrounds the isogenous groups -surrounds the territorial matrix and occupies the space between groups of chondrocytes |
|
|
Perichondrium:
-outer layer contains ___ -inner layer contains ___; It is eosinophylic because of |
-fibroblasts
-formative chondrocytes; type I collagen |
|
|
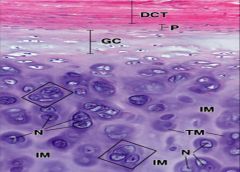
Hyaline Cartilage:
-GC – growing cartilage - Slightly basophilic, containing what? -What type of growth occurs here? |
-chondroblasts
-appositional growth |
|
|
hyaline:
immature chondrocytes at the periphery of the cartilage are |
elliptical
|
|
|
hyaline:
Chondrocytes can be located in |
lacunae (a small cavity or pit)
|
|
|
hyaline:
As the cells move deeper within the cartilage they appear |
rounded
|
|
|
hyaline:
Interstitial growth - mitotic division of a single chondrocytes can result in groups of up to eight chondrocytes called |
isogenous groups
|
|
|
hyaline:
Appositional growth |
differentiation of chondroblasts from the perichondrium (addition of new layers of cartilage upon older layers)
|
|
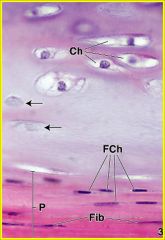
|
perichondrium
fibroblasts formative chondrocytes |
|
|
Epiphyseal plate is a disc of
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
In an H&E of young growing cartilage,
-the nucleus of chondrocyte is -clear area represents -ECM |
-eccentrically located
-golgi apparatus -basophilic |
|
|
In an EM of young growing cartilage
-abundant -extensive -many |
-rER
-GA -mitochondria indicating cell is actively producing ECM |
|
|
Elastic cartilage is found where?
|
-auricle
-external auditory meatus -eustacian tube -epiglottis -cartilage of larynx |
|
|
Elastic cartilage requires an ___ stain to differentiate itself from hyaline cartilage.
|
elastic, i.e. orcein or resorcein-fuschin
|
|
|
Like hyaline, elastin cartilage contains chondrocytes in
|
lacunae
|
|
|
ECM of elastic cartilage contains what?
|
elastic fibers and collagen type II fibrils
|
|
|
Does a perichondrium exist in elastic cartilage?
|
yes
|
|
|
Locations of fibrocartilage
|
-intervertebral disks (annulus fibrosis)
-symphysis pubis -meniscus of the knee -insertions of tendons and ligaments (sometimes) |
|
|
Fibrocartilage can be thought of as a hybrid (mixture) between
|
dense CT and cartilage
|
|
|
Does fibrocartilage contain chondrocytes in lacune like hyaline and elastic cartilage?
|
Yes
|
|
|
ECM of fibrocartilage contains
|
numerous collagen type I fibers
|
|
|
Like elastic and hyaline cartilage, does fibrocartilage contain a perichondrium?
|
NO
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage of intervertebral disc contains chondrocytes in lacunae, often arranged in
|
long rows (between the collagen bundles)
|
|
|
ECM of fibrocartilage of intervertebral disc
|
Contains numerous collagen type I fibers in addition to type II collagen fibers
|
|
|
Effects of cortisone, hydrocortisone on hyaline cartilage
|
Inhibits cartilage histogenesis, growth and matrix production
|
|
|
Effects of Vitamin C deficiency (Scurvy) on hyaline cartilage
|
matrix production stops --> distorts cartilage columns in epiphyseal plates
(Vitamin C is an enzyme cofactor required for collagen synthesis.) |

